Pharmacokinetics/Pharmacodynamics (PK/PD) of Antimicrobials and Novel Agents
A workshop for graduate students, pharmacy students, and postdocs
Jacob K. McPherson

University of Houston College of Pharmacy
October 21, 2025
Background Clinical Microbiology
You already know:
Minimum Inhibitory Concentrations (MIC)1
![]()
You already know:
Minimum Bactericidal Concentrations (MBC)2
![]()
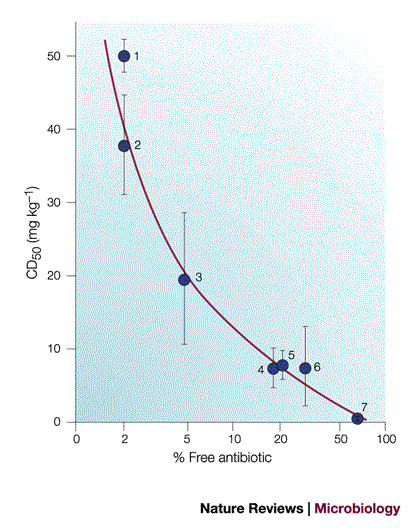
Only ‘Free’ Antibiotics are Microbiologically Active
Commonly used parameters
![]()
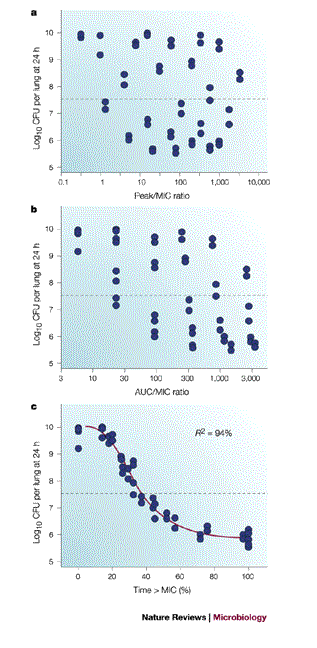
PK/PD Indices Predict Efficacy
Commonly used parameters
![]()
Pharmacokinetics (PK) 101
Fundamentals of Biopharmaceutics
Shargel and Yu’s Biopharmaceutics and Pharmacokinetics, 8th Edition, 2022
content
Drug distribution and protein binding
subtitle
content
Physiology of drug Elimination
subtitle
content
Introduction to PK/PD models
subtitle
One-compartment Open Model: IV bolus
Pharmacokineitcs of Drug Elimination and Clearance
Pharmacokinetics of Drug Absorption
Multiple-dosage regimens
subtitle
Nonlinear pharmacokinetics
subtitle
Empiric Models, Mechanistic Models, Statistical Moments, and Non-compartmental Models
subtitle
Relationship between Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics
subtitle
Application of Pharmacokinetics to Clinical Situations
subtitle
Application of Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics to Aging, Obese, and Pediatric Patients
subtitle
Dose Adjustment in Renal and Hepatic Diseases
subtitle
Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics in Clinical Drug Product Development
subtitle
Pre-clinical Models of Infection
The in vitro Hollow-Fiber Infection Model (HFIM)
subtitle
The in vivo Animal Models of Infection
subtitle
Six Clinical Cases
subtitle
Analysis of in vitro HFIM data
subtitle
Six Clinical Cases
subtitle
Analysis via PopPK
subtitle